Industrial activities are the primary cause of climate change, with greenhouse gas emissions growing exponentially since the Industrial Revolution.
This article explains how industries and factories contribute to global climate change.
What Causes Climate Change?
Climate change is caused by greenhouse gases trapping heat in the atmosphere, increasing the planet’s global temperature. The most prominent and influential greenhouse gases include:
- Carbon dioxide
- Methane
- Nitrous oxides
- Fluorinated gases
These chemicals are released into the atmosphere predominantly through the burning of fossil fuels for heat, electrical, and transportation purposes. Since the beginning of the Industrial Revolution, carbon dioxide emissions have increased exponentially, resulting in approximately 43 billion tons of carbon dioxide released annually.
While the earth has gone through many fluctuations in global temperatures over the course of the planet’s history, industrial emissions have resulted directly in temperatures rising far above the normal deviations.
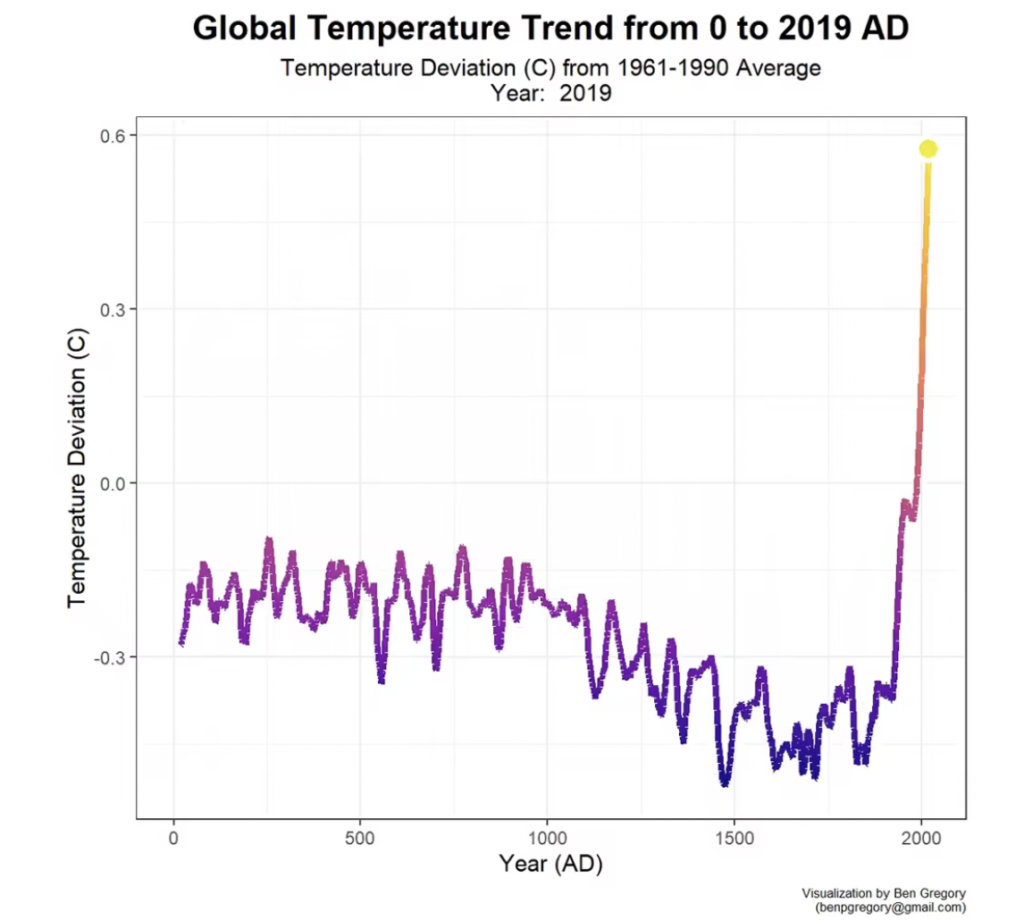
Rising global temperatures lead to a multitude of environmental catastrophes, including:
- Rising ocean levels due to melting glaciers and heated water expanding
- Extreme weather events (hurricanes, tornados, storms, etc.)
- Extreme heat and cold events
- Ecological instability
- Food and water scarcity
- Flood events
- Droughts
- Wildfires
Climate change is a direct result of greenhouse gas emissions and is a global crisis that affects every person on the planet, directly or indirectly. The consequences of climate change will continue to worsen as industrial activities continue.
How Do Industries Contribute to Climate Change?
Industrial activities are the leading cause of greenhouse gas emissions and climate change. Alone, manufacturing and industrial processes account for 20% of greenhouse gas emissions. Heat and energy production emits 49% of greenhouse gases, and transportation emits 20.5%. However, the majority of transportation and heat and energy emissions come directly from industrial activities.
Currently, the United States and China account for the highest amount of greenhouse gas emissions through their use of fossil fuel burning. Industrial emissions can be curbed through regulation and carbon offsetting; however, these are often difficult to implement and enforce on large scales, and more often result in factories submitting to federal fees instead of substantially reducing their emissions. Emissions can more effectively be reduced by the use of clean energy and avoiding the burning of oil, coal, and natural gases.
Individual emissions are substantially insignificant in comparison to industrial emissions, with the average American household producing 2.5e-8 % of global greenhouse gas emissions per year. However, individuals can influence climate change by their choice of consumption. By reducing the consumption of unsustainably produced goods, individuals can limit the ability of industries to contribute to greenhouse gas emissions.
What Industries Contribute the Most to Climate Change?
Fossil fuel production is the leading cause of climate change, which is used primarily by manufacturing and industry. While past narratives have focused heavily on individual carbon footprints, just 100 companies are directly responsible for 71% of carbon emissions. The top contributors include:
- ExxonMobile
- Shell
- Chevron
- Total
- BP
- Peabody
- BHP Billiton
These specific companies, along with other fossil fuel producers, are the primary cause of global climate change. In addition to fossil fuel producers, manufacturing industries also play a significant role in climate change. By requiring high amounts of fuel for heat and energy, manufacturers are among the primary consumers of fossil fuels. Industries that contribute the most to fossil fuel usage include:
- Clothing and textile industries
- Plastic production
The majority of the world’s clothing, textile, and plastic industries are located in areas with minimal regulations on greenhouse gas emissions, namely China. This results in higher emissions that are poorly mitigated, furthering the cause of climate change, as well as air pollution.
Read more: How Industrial Pollution Affects Global Air Quality
Industries that harvest timber resources also contribute to climate change by reducing natural forests, which are major barriers to climate change and natural offsets of atmospheric carbon. Deforestation accounts for approximately 30% of annual greenhouse gas emissions annually, with impacts expected to increase as deforestation increases.
Individual impacts to climate change are minimal; however, individuals can influence the industries that drive climate change. By choosing to purchase from sustainable companies that avoid fossil fuels and limit the impacts of their supply chains, individuals can limit the dependence on unsustainable production.
Read more: How Does Consumerism Drive Pollution?
