Factories and industries have a significant influence over the communities they impact.
While many of the impacts of factories can negatively affect local communities through pollution and human health, they can also substantially increase the livelihood of people by boosting local economies.
Learn how factories and increased jobs can benefit the economies and livelihoods of surrounding communities.
Driving Economic Growth
Industrialization is a complex issue with many positive and negative impacts on global and local populations. While factories can cause severe health and environmental concerns through pollution and poor working conditions, they can also create thousands of jobs and increase the livelihoods of local communities when managed responsibly and ethically.
Manufacturing is one of the biggest contributors to economic growth on the planet, with each dollar spent on manufacturing putting nearly twice the amount into larger economies. In many cases, this economic growth is funneled to a select wealthy few, while the factory workers and local communities see very little growth. Large industries can exploit small communities through low wages, harsh conditions, and long working hours. However, industries can greatly benefit small communities by creating economic booms and providing jobs and income to people who previously lacked financial stability.
Large-scale factories can provide hundreds to thousands of long-term jobs, opening up a gateway for smaller communities to access the profits and benefits of major manufacturing corporations. These externalities can extend beyond individual financial gain from factory jobs, and can pull large amounts of money into communities.
Read more: Positive and Negative Externalities of Industrialization
As manufacturing is one of the primary drivers of economies across the world, the promotion of industry results in the growth of other economic, political, and social factors. Growth in manufacturing in low-, middle-, and high-income nations results in direct increases in sustainable development goals (SDG), such as poverty reduction and education.
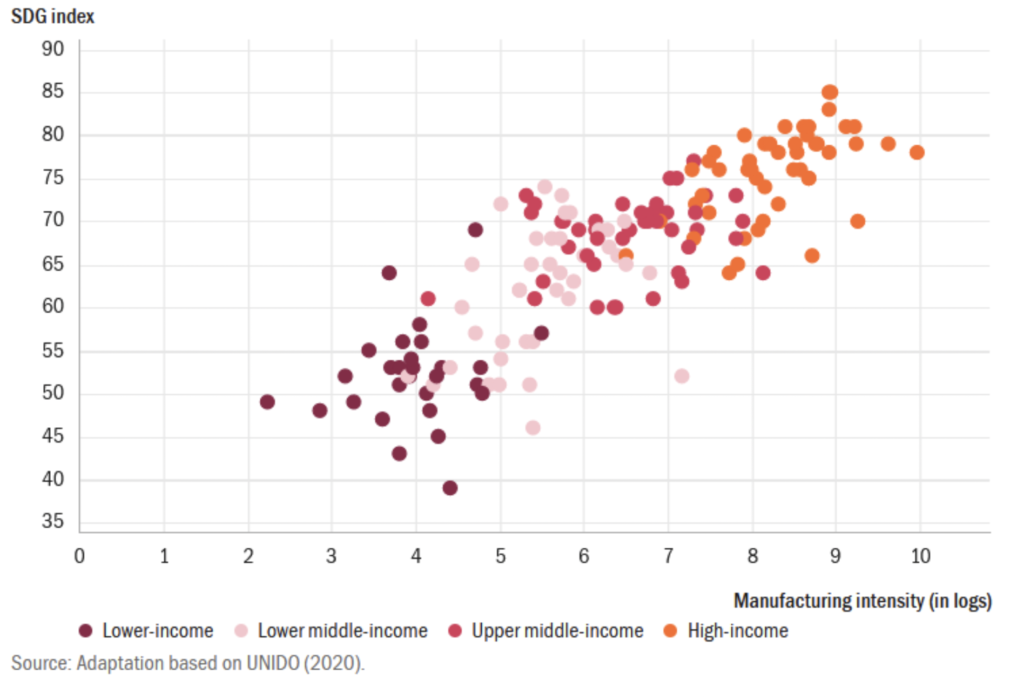
Benefits of Industries in Developed Nations
Local economies in developed nations benefit greatly from industries. In most developed countries, including Germany, Japan, the United Kingdom, and the United States, industries account for 10 – 20% of the national economy. Small communities and cities that are largely employed by factories receive positive externalities from these manufacturers in the form of:
- Stable jobs and income
- Medical benefits
- Trade skills
Additionally, the higher taxation rates allowed by greater employment in small communities leads to better funds for infrastructure and public services. These externalities directly lead to better schooling, safer infrastructure, and more available housing to further support the community. Benefits like these lead to long-term social benefits of steady community growth and the financial independence of residents.
Benefits of Industries in Developing Nations
In many developing countries, reliance on factory jobs is high, but many developing nations lack substantial labor laws and workers’ rights, allowing industries to exploit the poverty of their workers. However, when appropriately managed, industry can be a significant driver in local economies and can help funnel much-needed economic growth into communities that previously lacked it.
In developing countries, including Bangladesh and Indonesia, factories provide jobs to people who often lack substantial education and marketable skillsets, giving income to people who might otherwise struggle to find employment. While many industries exploit their workers through harsh working conditions and low wages, there are increasing pressures for improved working conditions and increased international trade standards.
Additionally, industrialization in developing nations helps bring in money from more affluent regions in the world, especially in countries like Kenya and Indonesia that may be unable to export other goods and services efficiently. This helps developing nations and local factory communities benefit from global supply chains and markets that have historically been inaccessible to them.
While many factories around the world still suffer from poor conditions and exploited workers, the continuously improving factory conditions will further help industries improve the livelihood of local communities and economies across the world.
Read more: Improving Worldwide Factory Conditions
